Blog
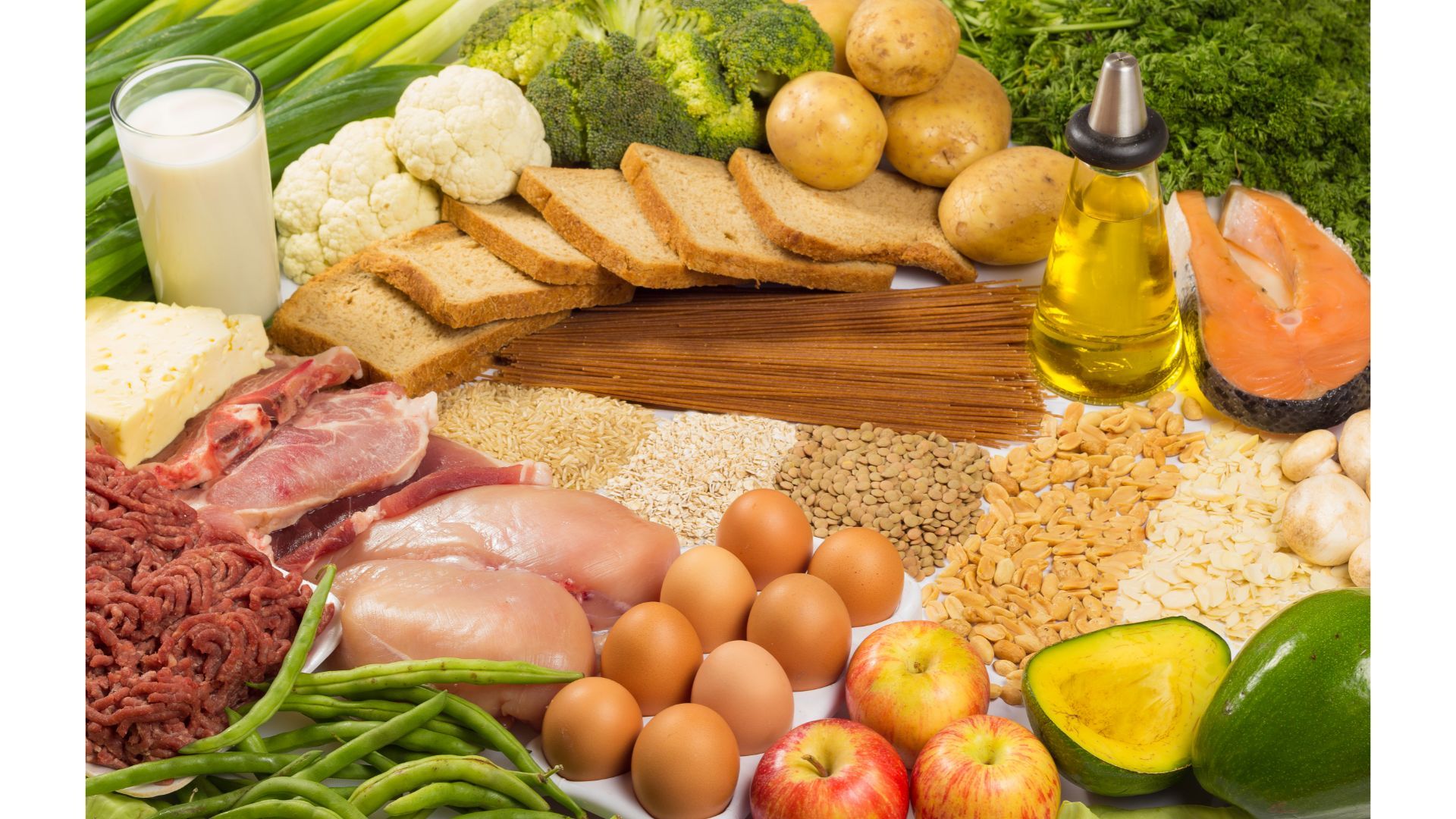

Macronutrients are the foundation of our dietary choices, providing the body with the essential elements needed for optimal functioning. Water, protein, carbohydrates, fats, and fiber are the key macronutrients that fuel our bodies. In this in-depth guide, we'll explore the significance of each macronutrient, their dietary sources, and their roles in maintaining overall health. Understanding macronutrients is essential for making informed dietary decisions that promote well-being. The Vital Role of Water Water, often overlooked as a macronutrient, is the most crucial nutrient for sustaining life. It is the universal solvent, responsible for countless biological processes. Here are some key facts about water as a macronutrient: Importance: Water constitutes more than two-thirds of the human body's weight and is essential for life. Functions: It serves as the basis for bodily fluids, including blood, saliva, and joint fluids. Water regulates body temperature through perspiration and aids in digestion, helping to move food through the intestinal tract and eliminating waste from the body. Dehydration: Dehydration can have severe consequences, including cognitive impairment and organ dysfunction. Adequate hydration is vital for overall health and should not be underestimated. Protein: The Building Blocks of Life Protein is a fundamental macronutrient that forms the basis of life. It is composed of amino acids and plays a variety of crucial roles in the body. Here's what you need to know about protein: Functions: Proteins are the building blocks of enzymes, antibodies, and hormones. They transport nutrients, oxygen, and waste throughout the body and provide structural support for muscles, connective tissues, skin, hair, and nails. Sources: Proteins can be obtained from various sources, including meats, dairy products, vegetable proteins, and protein supplements. Amino Acids: Proteins are made up of amino acids. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be supplied through the diet. Complete proteins contain all essential amino acids, while incomplete proteins do not. Diverse Sources of Protein Protein can be sourced from a variety of foods, including: Meats: Lean poultry (such as chicken and turkey), red meats (lean cuts like beef), pork, lamb, fish (like cod, snapper, and salmon), and shellfish (mussels, oysters, scallops, prawns, lobsters). Dairy: Options include milk, low-fat cottage cheese, natural yoghurt, cheeses (choose softer varieties), and eggs (egg whites are pure protein). Vegetable Proteins: Raw nuts and seeds (rich in healthy fats and carbohydrates), grain protein (found in grains like wheat and rice), and bean/vegetable protein (soybeans are a primary source). Protein Supplements: These include whey protein (fast-digesting), casein protein (slow-digesting), soy protein (derived from soybeans), egg protein (primarily albumin), and vegetable proteins like wheat and pea protein. Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, can be found in various forms. Carbohydrates: The Body's Energy Source Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body, necessary for various bodily functions. Here's what you should know about carbohydrates: Importance: Carbohydrates provide the energy required for all bodily functions, including muscular exertion. They also help regulate protein and fat metabolism. Types: Carbohydrates can be categorized into simple and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates include sugars like fructose, glucose, and lactose, while complex carbohydrates are found in foods like grains, vegetables, and legumes. Sources: Carbohydrates are abundant in foods like potatoes, fruits, grains, and whole-grain products. They are essential for growth and tissue repair. A World of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates can be classified into two main categories: Simple Carbohydrates: Sugar Cane & Sugar Beets (the main commercial sources of sugar) Fresh Fruit & Berries (containing mainly fructose, a low-GI sugar) Honey (a mix of glucose and fructose) Milk and milk products (containing lactose) Prepared sugars (glucose, fructose, lactose, maltose, found in drinks or free form) Complex Carbohydrates: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, and squash Yams, parsnips, and other root vegetables Corn, oats, wheat, and other grains Whole-grain flours, breads, and pastas Brans, Weet Bix, and shredded wheat cereals Ancient grains (amaranth, millet, teff, etc.) Basmati, brown, and wild rice Raw nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, couscous, and other pulses Vegetables such as carrots and peas Fats/Oils: Energy-Dense Macronutrients Fats, often referred to as lipids, are energy-dense macronutrients that serve various vital functions in the body. Here's what you should know about fats: Functions: Fats are critical for building cell membranes, providing a source of energy, and supporting the transmission of nerve impulses. They are also involved in hormone synthesis and brain function. Types: Fats can be classified as saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated, based on their molecular structure. Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) are a subset of fats that the body cannot produce on its own and must be obtained from the diet. Sources: Fats are found in both plant and animal sources. Plant-based fats can be found in oils like olive and canola oil, as well as nuts and seeds. Animal-based fats are present in fatty fish, dairy products, and lean meat. Diverse Sources of Fats Fats can be sourced from a variety of foods, including: Vegetable Fat Sources: Flaxseed, hempseed, evening primrose, almond, canola, olive, and most other plant oils. Whole raw nuts and seeds (some seeds need to be cracked or ground for digestion). MCT oils (medium-chain saturated fats derived from coconut oil, available as a supplement). Animal Fat Sources: Fatty fish like salmon, cod, halibut, and shellfish (rich in unsaturated fats and EFAs). Dairy products (fat content can vary widely and may contain saturated fat). Lean meat and poultry (even when trimmed and skinless, they provide fat and can be high in saturated fat). Eggs (only the yolk contains primarily saturated fat). Fiber: The Non-Caloric Macronutrient Fiber is a unique macronutrient because it doesn't provide calories, yet it plays a crucial role in digestive health. Here's what you need to know about fiber: Types of Fiber: Soluble Fiber: These fibers can dissolve in water and have a thickening effect, slowing down digestion and supporting artery health. Insoluble Fiber: These fibers, such as cellulose, do not dissolve in water and do not affect the speed of digestion. They are beneficial to gut health. Diverse Sources of Fiber Fiber can be found in various foods, including: Broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage Celery, lettuce, spinach, watercress Mushrooms, onions, carrots Green beans, peas, asparagus, kale Bean and vegetable sprouts, beetroot, leeks Cucumber, zucchini, aubergine Tomato, capsicum, silverbeet Frozen mixed vegetables Any non-starchy vegetable of any color Any grain or grain product Fruits and berries Legumes Understanding macronutrients is essential for making informed dietary choices. Water, protein, carbohydrates, fats, and fiber all play significant roles in maintaining overall health. While water is often overlooked as a macronutrient, it is indispensable for life and should be prioritized. Protein is the building block of life, and a variety of sources provide the amino acids our bodies need. Carbohydrates provide the primary source of energy, and the type of carbohydrates we consume can impact our health. Fats are energy-dense and serve crucial functions, including brain health. Fiber, while not a source of calories, supports digestive health and overall well-being. By balancing and incorporating these macronutrients into your diet, you can ensure that your body receives the energy and nutrients it needs to function optimally. A well-rounded and balanced diet that includes all essential macronutrients is key to maintaining good health throughout your life.
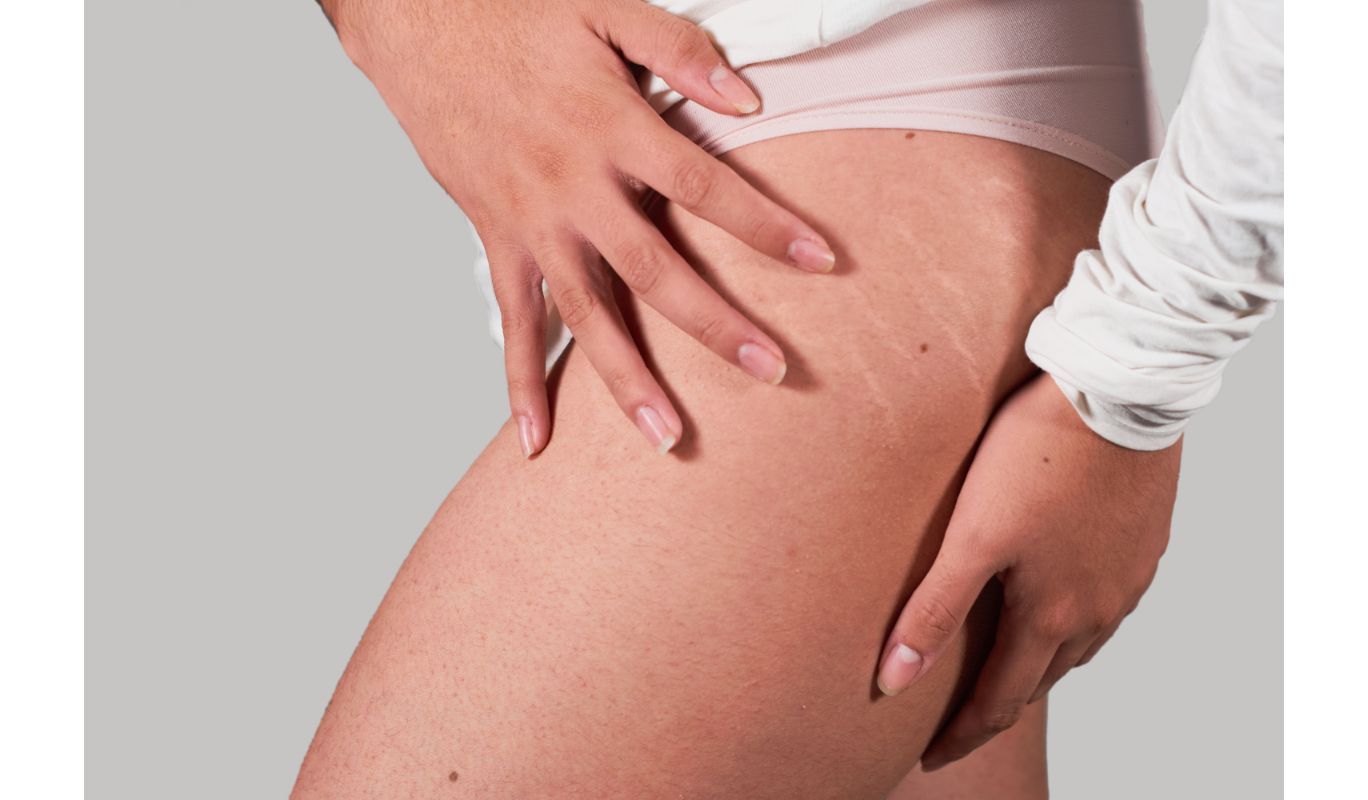
Stretch marks, scientifically known as striae, are a common concern for many individuals. These skin imperfections often develop due to rapid changes in body size, such as weight gain or pregnancy. While they are a natural part of life, they can be bothersome for those who wish to minimize their appearance or prevent them altogether. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore effective methods to prevent and treat stretch marks. We will also debunk some common myths and provide fact-checked information to ensure you have accurate guidance. Understanding Stretch Marks Before delving into prevention and treatment strategies, it's crucial to understand what stretch marks are and why they occur. Stretch marks are caused by the stretching of the skin beyond its normal limits, leading to the breakdown of collagen and elastin, which are the support structures of the skin. When these fibers are damaged, it results in the formation of stretch marks. Factors contributing to stretch marks include: Rapid Weight Changes: Sudden weight gain or loss can strain the skin, causing it to stretch and potentially tear. Pregnancy: The skin on the abdomen stretches significantly during pregnancy, making it a common time for stretch marks to develop. Puberty: Adolescents experiencing growth spurts may develop stretch marks as their bodies rapidly change in size. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during puberty and pregnancy, can weaken the skin's elasticity. Now that we have a clear understanding of what causes stretch marks let's explore various methods to prevent and treat them. Hydration: The Role of Water in Preventing Stretch Marks One common misconception is that drinking an excessive amount of water can prevent stretch marks. While hydration is essential for overall skin health, there is no evidence to support the idea that consuming large volumes of water can prevent stretch marks. However, staying adequately hydrated can help keep your skin in good condition and maintain its natural elasticity. Drinking an appropriate amount of water daily (approximately 8-10 glasses or 2-2.5 liters) is recommended for general skin health. Cocoa Butter for Stretch Marks: Myth or Reality? Cocoa butter has gained popularity as a remedy for preventing and treating stretch marks. Some cocoa butter products, like Palmer's Cocoa Butter, contain ingredients like vitamin E, collagen, and elastin, which are believed to support skin health. While cocoa butter is often used in skincare routines, there is limited scientific evidence to prove its effectiveness in preventing or reducing stretch marks. Nevertheless, applying cocoa butter daily can help keep the skin moisturized and may improve its appearance. The Role of Vitamins and Minerals Vitamins and minerals play a vital role in maintaining healthy skin and may contribute to the prevention and reduction of stretch marks. However, it's important to note that while these nutrients are essential for overall health, they should not be solely relied upon as a magic solution for stretch marks. Vitamin A: Vitamin A is crucial for skin growth, repair, and maintenance. It is known to stimulate the skin's renewal process, which can improve skin thickness and elasticity. While topical application of vitamin A can be beneficial, it should be used cautiously, as excessive use can lead to skin irritation. Vitamin C: Vitamin C is essential for wound healing and the synthesis of collagen, which is a key structural protein in the skin. However, vitamin C is most effective when obtained from a balanced diet rather than through topical application, as it may lose its potency when exposed to air and light. Vitamin E: Vitamin E is an antioxidant that can help protect and heal skin tissues. It is commonly used to aid in the recovery process of post-surgical scars. Applying vitamin E topically or taking it orally can be beneficial for skin health. Zinc: Zinc is a critical mineral for the production of collagen, the protein responsible for skin tissue strength and elasticity. Collagen makes up a significant portion of the skin's structure, and adequate zinc intake can help maintain healthy skin. However, collagen is not available in food, so supplementation with zinc may be necessary. Preventing Stretch Marks: Fact-Checked Tips Prevention is often more effective than trying to treat existing stretch marks. Here are some fact-checked tips to help prevent stretch marks: Maintain a Balanced Diet: A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins and minerals, can support overall skin health. Incorporate fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your meals. Gradual Weight Changes: Avoid rapid fluctuations in body weight, as they can strain the skin and increase the risk of developing stretch marks. Aim for gradual, sustainable changes when losing or gaining weight. Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise can improve blood circulation and promote skin health. Exercise also plays a role in maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the likelihood of stretch marks. Skin Moisturization: Keeping the skin well-moisturized with a high-quality lotion or cream can enhance skin elasticity and reduce the chances of developing stretch marks. Stretch marks are a common concern for many, but understanding their causes and employing effective prevention strategies can help minimize their impact. While vitamins, minerals, and skincare products play a role in skin health, they should be considered as part of a holistic approach to maintaining healthy skin. Maintaining proper hydration, engaging in a balanced diet, gradual weight management, regular exercise, and skin moisturization are all essential elements of preventing stretch marks. By following these fact-checked tips, you can increase your chances of maintaining smooth and healthy skin throughout life. Remember that preventing stretch marks is a holistic process that encompasses various aspects of health and skincare.

In the pursuit of a healthier, more balanced lifestyle, many individuals often find themselves on a journey that involves managing their body weight. It can be frustrating when, despite putting in hard work and adhering to a healthy diet, the numbers on the scale seem uncooperative. However, it's essential to recognize that body weight is subject to regular fluctuations influenced by various factors. This article delves into the intricacies of weight fluctuation, discusses the reasons behind it, and explores alternative methods to measure your progress more accurately. By understanding these nuances, you can gain a more comprehensive perspective on your health and fitness journey. Understanding Weight Fluctuation The journey to a healthier you can often be hindered by the stubborn readings on the scale. These fluctuations are perfectly normal and can range from 1 to 2 kilograms over the course of a few days, causing inaccuracies in your weight measurements. To truly grasp the significance of these fluctuations, it's crucial to explore the reasons behind them: Water, Carb, or Sodium Intake: The consumption of foods high in sodium or carbohydrates can lead to temporary water retention, reflecting as an increase in weight on the scale. Bowel Movements: Regular bowel movements can lead to weight changes, especially if you've recently eliminated waste from your body. Sleeping Habits (Lack of Sleep): Poor sleep patterns can disrupt hormonal balance, potentially affecting your weight and metabolism. Menstrual Cycle: For women, weight fluctuations are often linked to the menstrual cycle due to hormonal changes and water retention. Time of the Day: Your weight can vary throughout the day, with it usually being lower in the morning and higher in the evening. Change in Your Training Routine (Intensity): Intense workouts, which may cause muscle inflammation and temporary fluid retention, can influence the scale's reading. Stress: Elevated stress levels can trigger hormonal responses that affect weight and metabolism. Medication: Some medications can lead to weight gain or loss as a side effect. Glycogen Levels: The body stores energy in the form of glycogen, which can lead to fluctuations in weight based on glycogen levels. Illness: Illness, inflammation, or infections can also lead to changes in body weight as the body's response to these conditions. These factors collectively highlight the dynamic nature of body weight and why it's subject to regular variations. Therefore, it's important to view the scale as a tool for tracking your overall transformation but not the sole determinant of your progress. Consistency in Weighing To make the most of the scale as a tracking tool, consistency is key. We recommend weighing yourself under specific conditions, such as first thing in the morning, after using the bathroom, and before eating. Consistency ensures that your measurements are as accurate as possible, as weighing yourself at different times can yield inconsistent and unreliable results. Maintaining a routine for weighing yourself helps you better understand your body's natural fluctuations. Alternative Methods of Measurement While the scale is a valuable tool, it's not the only one available for tracking your progress. Alternative methods can provide a more comprehensive view of your body's transformation. Here are some effective alternatives: Body Measurements: Tracking the size of your arms, waist, hips, and thighs can reveal how your body is changing. Even if the scale shows no significant weight difference, these measurements may indicate progress, especially if your goal is to decrease or increase specific areas of your body. Progress Photos: Taking photographs of your body composition before starting your transformation offers an accurate starting point. These photos can serve as visual evidence of your progress, even when the numbers on the scale don't seem to budge. Comparing these photos over time can be motivating and reassuring. Body Fat Percentage: Body fat percentage measurements, using tools like skinfold calipers or bioelectrical impedance scales, provide a more accurate representation of your body composition than weight alone. These measurements can help you track changes in your fat and muscle mass. Fitness Assessments: Regular fitness assessments, including strength, endurance, and flexibility tests, can reveal improvements in your physical fitness, even if your weight remains relatively stable. Clothing Fit: Pay attention to how your clothing fits. If your clothes become looser or you drop a clothing size, it's a clear sign of positive change, regardless of what the scale says. Realistic Expectations It's important to maintain realistic expectations when using any method to measure your progress. Weight loss and fitness journeys are highly individualized, and progress can occur at different rates for each person. Rapid, significant weight loss is often unsustainable and can be metabolically harmful. Healthy and sustainable change takes time and patience. Remember that the number on the scale is just one aspect of your overall health and should not be the sole determinant of your success. In your quest for a healthier and more vibrant you, understanding the intricacies of weight fluctuation is paramount. The numbers on the scale can be influenced by numerous factors, and it's essential to view them in the context of your overall health journey. Consistency in weighing, coupled with alternative methods of measurement like body measurements, progress photos, body fat percentage, fitness assessments, and clothing fit, can provide a more accurate picture of your progress. By adopting realistic expectations and recognizing that your transformation is a unique and ongoing process, you can stay motivated and focused on your goals. The scale may fluctuate, but your commitment to a healthier lifestyle is what truly matters. Embrace the journey, celebrate the small victories, and stay dedicated to your well-being.

Key Takeaways: The link between sleep and weight loss: Sufficient sleep plays a crucial role in weight loss. Lack of sleep can hinder weight loss efforts and increase the likelihood of weight gain. The impact of short sleep duration: Not getting enough sleep can lead to weight gain and obesity. Short sleep duration is associated with increased body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference. The connection between sleep and hunger: Sleep deprivation can disrupt the hormones that regulate hunger, leading to increased appetite. Poor sleep affects levels of ghrelin and leptin, hormones that influence appetite. Sleep's influence on food choices and self-control: Sleep deprivation impairs decision-making abilities and affects brain responses to food rewards. It also weakens self-control, making it harder to resist unhealthy food choices. Avoiding late-night snacking through better sleep habits: Sleep habits, including bedtime, can impact late-night eating. Sleep deprivation can lead to poor food choices at night. Strategies for improving sleep can help control late-night snacking. Prioritizing sleep for successful weight loss: To achieve successful weight loss, it is important to prioritize and prioritize sufficient sleep. Adequate sleep supports weight loss efforts and promotes overall health. The Role of Sleep in Weight Loss Let's dive into the fascinating connection between sleep and weight loss. According to recent studies from reputable sources, such as the National Sleep Foundation and the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the link between sleepand weight loss is undeniable. In this section, I'll unravel the intriguing findings and shed light on how a restful night's sleep can potentially enhance your weight loss journey. So grab a cozy blanket and get ready to uncover the importance of sleep when it comes to shedding those extra pounds. The Link Between Sleep and Weight Loss " Sleep plays a crucial role in weight loss as it has a direct and significant link to our body's ability to shed those extra pounds. Short sleep duration, for instance, has been consistently associated with weight gain and increased risk of obesity. Research findings have shown that individuals with shorter sleep duration tend to have higher BMI and larger waist circumference, indicating a clear connection between sleep deprivation and weight-related factors. Moreover, lack of sufficient sleep disrupts the balance of hormones like ghrelin and leptin, which regulate hunger and appetite. Consequently, poor sleep can lead to higher levels of hunger and lower feelings of fullness, making it challenging to maintain a healthy diet and control food choices. Furthermore, studies have revealed that sleep deprivation impairs decision-making abilities, particularly when it comes to food choices and self-control. Individuals who are sleep-deprived tend to exhibit stronger brain responses to food rewards, making it more difficult to resist unhealthy snacks or overeating. In order to avoid late-night snacking, establishing better sleep habits is essential. For instance, maintaining a regular bedtime can help regulate circadian rhythms and reduce the likelihood of engaging in nighttime eating. Additionally, improving sleep quality can also lead to healthier food choices at night by reducing cravings for high-calorie foods. Strategies such as creating a relaxing bedtime routine or optimizing the bedroom environment can contribute significantly to overall better sleep hygiene. Hence, prioritizing adequate and quality sleep is paramount when aiming for successful weight loss as it not only influences various physiological factors but also impacts our food choices, self-control, and overall well-being. Lose sleep, gain weight - a terrible trade-off that puts your dreams of a trim waistline in jeopardy. " Short Sleep Duration and Weight Gain When it comes to weight loss, sleep duration plays a crucial role that often goes overlooked. In this section, we will explore the impact of short sleep duration on weight gain and its correlation with body mass index (BMI) and obesity risk. Additionally, we will examine the association between insufficient sleep and waist circumference, shedding light on how lack of sleep can affect our body shape. Furthermore, we'll dive into research findings specifically focusing on children and adolescents, highlighting the importance of adequate sleep in this demographic for healthy weight management. The Impact of Short Sleep Duration on BMI and Obesity Risk The effects of inadequate sleep on BMI and obesity risk are significant. Insufficient sleep duration can have a detrimental impact on body weight and increase the likelihood of developing obesity. Studies have shown that shorter sleep duration is associated with higher BMI and waist circumference, both indicators of obesity. This connection holds true for both adults and children, highlighting the importance of adequate sleep in maintaining a healthy weight. Lack of sleep not only influences body weight but also affects hunger levels. Sleep deprivation has been found to increase ghrelin levels, which stimulates appetite, while decreasing leptin levels, which signals fullness. These hormonal changes can lead to increased hunger and overeating, further contributing to weight gain. Additionally, poor sleep quality and quantity can impair decision-making abilities, making it harder to resist unhealthy food choices. To mitigate the impact of short sleep duration on BMI and obesity risk, several strategies can be implemented. Setting a consistent bedtime routine can promote better sleep habits and ensure an adequate duration of sleep each night. Creating a conducive sleeping environment by limiting noise, light exposure, and electronic devices can also improve the quality of restful sleep. Moreover, incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines helps regulate hormones that affect appetite and metabolism. Exercise has been proven to improve overall sleep quality as well as enhance weight loss efforts. Finally, managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises can aid in achieving better sleep patterns and reducing the risk of weight gain associated with insufficient rest. A short sleep duration not only adds inches to your waistline but also reduces your chances of fitting into your old jeans. The Association Between Short Sleep Duration and Waist Circumference A strong link exists between the duration of sleep and waist circumference. Shorter sleep duration is associated with an increase in waist circumference, indicating a potential risk for obesity. This association applies not only to adults but also to children and adolescents. When individuals do not get enough sleep, their hormonal balance is disrupted, resulting in increased hunger levels and decreased fullness. The impact of these hormonal changes can lead to poor food choices and impaired self-control, particularly when it comes to late-night snacking. It is crucial to prioritize adequate sleep for successful weight loss and to maintain a healthy waist circumference. Sleep deprivation consistently showed its adverse effects on weight gain in various studies conducted over the years. A true history lies in the fact that individuals who slept less had a higher risk of obesity due to the effects on hunger hormone regulation, reduced decision-making ability, and altered brain responses to food rewards. Therefore, improving sleep habits becomes essential for controlling late-night snacking and overall weight management. A good night's sleep isn't just for adults, even kids and teens need quality slumber to stay slim. Research Findings in Children and Adolescents Sleep and its impact on weight loss have been extensively studied, including research findings in children and adolescents. This specific age group is important to consider, as it provides valuable insights into the connection between sleep and weight among young individuals. By analyzing various studies, researchers have identified significant correlations between sleep patterns and weight-related outcomes in this population. StudyParticipant SizeSleep DurationWeight StatusStudy 110007-8 hoursLower obesity riskStudy 2500<6 hoursHigher BMI and waist circumferenceStudy 3800Inadequate sleepIncreased likelihood of being overweight These findings suggest that insufficient sleep duration among children and adolescents is associated with an increased risk of obesity, higher body mass index (BMI), and larger waist circumference. Furthermore, inadequate sleep has been found to contribute to an increased likelihood of being overweight in this age group. Pro Tip: Encouraging sufficient sleep duration in children and adolescents can be a crucial factor in preventing weight gain and promoting healthy weight management. Lack of sleep turns your stomach into an all-you-can-eat buffet. The Connection Between Sleep and Hunger When it comes to losing weight, many of us focus primarily on diet and exercise, often overlooking a crucial piece of the puzzle: sleep. In this section, we'll delve into the fascinating connection between sleep and hunger. We'll explore how sleep deprivation affects your hunger levels, the role of hormones like ghrelin and leptin in sleep and appetite regulation, and other hormonal effects of poor sleep on your feelings of hunger and fullness. Understanding this connection is essential for anyone striving to achieve their weight loss goals. So let's dive in and explore the impact of sleep on our appetite. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, participants who were sleep-deprived experienced an increase in their hunger levels throughout the day. Similarly, a study conducted at the University of Chicago found that sleep deprivation led to an increase in ghrelin, the hormone responsible for signaling hunger, and a decrease in leptin, the hormone that signals fullness. These findings highlight the intricate relationship between sleep and our appetite hormones. Additionally, poor sleep can disrupt the balance of other hormones involved in regulating our hunger and fullness cues, such as insulin and cortisol, leading to further imbalances in our eating patterns. So, join me as we explore the impact of sleep on our hunger and how prioritizing quality sleep can positively affect our weight loss journey. How Sleep Deprivation Affects Hunger Levels Lack of sleep can impact hunger levels significantly. Sleep deprivation has been found to increase appetite and cravings, especially for high-calorie foods. It affects the production of ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite, and leptin, a hormone that signals fullness. Poor sleep also disrupts other hormones involved in hunger and satiety regulation. As a result, individuals who are sleep-deprived tend to consume more food and may struggle with weight management. The connection between sleep deprivation and hunger levels is further supported by research findings. Studies have shown that sleep restriction leads to increased feelings of hunger, particularly for carbohydrate-rich foods. This is attributed to alterations in brain activity patterns related to food reward processing. Additionally, sleep deprivation affects decision-making abilities, making it harder to resist tempting food choices and exert self-control. Moreover, the timing of sleep can also influence late-night snacking. Irregular bedtime patterns have been associated with higher calorie intake during nighttime hours. Lack of adequate rest causes individuals to lean towards energy-dense snacks as a means of compensating for fatigue and maintaining alertness. Intriguingly, adopting better sleep habits can aid in controlling late-night snacking. Establishing a consistent bedtime routine, creating a conducive sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bed can improve the quantity and quality of sleep experienced each night. Understanding how sleep deprivation affects hunger levels sheds light on the importance of prioritizing adequate rest when aiming for successful weight loss journeys. By addressing both proper nutrition and sufficient sleep, individuals can optimize their chances of effectively managing hunger levels and achieving their weight loss goals. Ghrelin and leptin: the hormonal power couple that can make or break your sleep and appetite relationship. The Role of Ghrelin and Leptin in Sleep and Appetite The connection between ghrelin and leptin hormones and their role in regulating sleep and appetite has been extensively studied. Ghrelin is known as the "hunger hormone" as it stimulates appetite, while leptin is the "satiety hormone" that signals fullness. Research suggests that sleep deprivation can disrupt the balance of these hormones, leading to increased ghrelin levels and decreased leptin levels. This imbalance can result in higher levels of hunger and cravings for unhealthy food choices. Additionally, poor sleep quality can impair the sensitivity of brain regions involved in decision making, further contributing to unhealthy eating behaviors. Thus, prioritizing quality sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance of ghrelin and leptin hormones, which can help regulate appetite and support successful weight loss efforts. Incorporating strategies to improve sleep hygiene, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleeping environment, may help regulate ghrelin and leptin levels. Additionally, avoiding late-night snacking by aligning bedtime with the body's natural circadian rhythms can further promote weight loss goals. By understanding the intricate relationship between ghrelin, leptin, sleep, and appetite regulation, individuals can prioritize adequate sleep as an important factor in achieving successful weight loss outcomes. Previous research has highlighted the impact of sleep deprivation on overall cognitive function. However, specific attention should be directed towards its effect on food-related decision making processes. Sleep deprivation has been shown to impair self-control mechanisms when it comes to making healthier food choices. This can lead to increased consumption of high-calorie foods that are typically associated with weight gain. A study conducted among college students found that those who were deprived of adequate nighttime sleep showed increased activation in brain regions associated with reward seeking when presented with images of high-calorie foods compared to those who had sufficient sleep. This heightened reward response may explain why individuals tend to make impulsive and less healthy food choices when sleep-deprived. In summary, research suggests that the role of ghrelin and leptin in sleep and appetite is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight. Sleep deprivation disrupts the balance of these hormones, leading to increased hunger levels, impaired decision making, and a preference for unhealthy food choices. Prioritizing sufficient, quality sleep is essential for regulating ghrelin and leptin levels, supporting weight loss efforts, and promoting overall health and well-being. Lack of sleep can turn you into a human vacuum cleaner, constantly hungry and oblivious to the concept of fullness. Other Hormonal Effects of Poor Sleep on Hunger and Fullness Numerous hormonal effects arise as a result of poor sleep, influencing hunger and fullness. Sleep deprivation is associated with changes in ghrelin and leptin levels, altering appetite regulation. Additionally, disturbed sleep impacts the release of other hormones that regulate hunger and satiety, such as cortisol and insulin. These hormonal imbalances caused by poor sleep contribute to increased cravings, overeating, and difficulty feeling satisfied after meals. Moreover, studies have shown that individuals who experience insufficient sleep tend to have higher levels of ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite. Conversely, leptin levels decrease with lack of sleep. Leptin is responsible for signaling fullness to the brain. The dysregulation of these hormones due to poor sleep can lead to an increase in hunger and a reduced ability to control food intake. Furthermore, poor sleep quality and duration have been associated with dysfunctions in insulin production and cortisol release. These two hormones play essential roles in regulating blood sugar levels and stress response respectively but may also affect hunger sensations. Irregular insulin responses can disrupt glucose metabolism and potentially lead to increased hunger or cravings for high-sugar foods. Similarly, elevated cortisol levels linked to poor sleep contribute to heightened appetite and a preference for calorie-dense foods. It is important to note that these hormonal effects do not operate in isolation but rather interact with one another, creating a complex relationship between sleep quality, hormone regulation, hunger sensations, and food choices. Therefore, prioritizing healthy sleep patterns should be considered alongside dietary changes when aiming for successful weight loss. Pro Tip: Prioritizing adequate and high-quality sleep can support weight loss efforts by helping maintain optimal hormonal balance for hunger regulation. Focus on establishing a consistent bedtime routine and creating a conducive sleeping environment to enhance both sleep duration and quality. Sleep well or snack hard - the power of a good night's sleep on controlling those late-night cravings. Sleep's Influence on Food Choices and Self-Control <\p>When it comes to losing weight, we often focus on exercise and diet, but there's another crucial factor that we tend to overlook: sleep. In this section, I want to highlight the significant influence that sleep has on our food choices and self-control. Prepare to be surprised as we explore the impact of sleep deprivation on decision making, how sleep affects our brain's responses to food rewards, and the link between sleep deprivation and impaired self-control. Understanding these connections can help us prioritize quality sleep as a key component of our weight loss journey.<\p> The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Decision Making Sleep Deprivation's Influence on Decision Making: Lack of sleep significantly affects decision making abilities. When deprived of sufficient sleep, individuals tend to exhibit impaired cognitive functions, such as reduced attention and concentration levels. This can result in poor judgment, lower inhibitions, and increased risk-taking behaviors. In addition, sleep deprivation hinders the ability to assess risks accurately and make rational choices. The impact of sleep deprivation on decision making can be detrimental in various aspects of life, including personal relationships, work performance, and overall well-being. Furthermore, research has shown that inadequate sleep diminishes activity in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, affecting its ability to regulate emotions and make sound decisions. As a result, individuals experiencing sleep deprivation may struggle with assessing the long-term consequences of their actions or evaluating alternative solutions effectively. Additionally, they may experience difficulties in prioritizing tasks and managing time efficiently. It is important to note that the impact of sleep deprivation on decision making is not isolated to professional or academic settings alone. Everyday tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery require alertness and sound judgment – both of which are compromised when one is sleep-deprived. This poses serious safety concerns not only for themselves but also for those around them. To mitigate the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation on decision-making abilities, it is crucial to prioritize quality sleep by adhering to healthy sleeping habits. This includes following a consistent sleep schedule, creating a conducive sleeping environment free from distractions, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, and avoiding stimulants close to bedtime. Pro Tip: Prioritizing sufficient restorative sleep enables individuals to optimize their cognitive functions and make informed decisions across different areas of life while minimizing the risks associated with compromised judgment due to lack of sleep. Sleep doesn't just help you dream about food, it also helps your brain resist the temptation to eat it. The Effect of Sleep on Brain Responses to Food Rewards Sleep's Impact on Brain Reactions to Food Incentives: Sleep significantly influences the way our brain responds to food rewards. Numerous studies have explored the effect of sleep on brain responses to food incentives. Research findings consistently indicate that inadequate sleep or sleep deprivation alters neural activity in regions associated with reward processing, thus affecting our response to food. During periods of insufficient sleep, the brain exhibits heightened activation in areas responsible for processing hedonic aspects of food, such as the prefrontal cortex and striatum. These regions influence appetite regulation and decision making related to food choices. Consequently, sleep-deprived individuals tend to exhibit increased desire for high-calorie foods and reduced self-control when faced with tempting food options. Moreover, lack of sleep disrupts the balance of hormones involved in appetite regulation. Ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates hunger, is elevated while leptin, a hormone that promotes satiety and fullness, is decreased with insufficient sleep. This hormonal imbalance further contributes to intensified cravings for unhealthy foods and overeating. Interestingly, research has also shown that poor sleep negatively impacts areas of the brain associated with impulse control and decision making. Sleep deprivation impairs cognitive processes involved in evaluating long-term consequences and inhibits impulsive responses. As a result, individuals are more likely to make unhealthy food choices and succumb to late-night snacking. In a study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, it was found that participants who slept less than seven hours per night exhibited stronger activation in reward-related brain regions when exposed to images of palatable foods compared to those who had adequate sleep. This demonstrates how even short-term sleep restriction can lead to increased responsiveness towards rewarding foods. Therefore, prioritizing sufficient and quality sleep is crucial when aiming for successful weight loss. By ensuring an adequate amount of restorative sleep each night, individuals can optimize their brain's response to food rewards and enhance their ability to make healthier food choices throughout the day. Sleep deprivation turns even the most disciplined dieter into a midnight snack monster. Sleep Deprivation and Impaired Self-Control Sleep deprivation can have a detrimental impact on self-control, leading to impaired decision-making and weakened resistance to temptation. When individuals do not get enough sleep, their ability to regulate impulses and make rational choices becomes compromised. This lack of self-control can manifest in various ways, such as difficulty in resisting unhealthy foods or succumbing to late-night snacking urges. Studies have shown that sleep deprivation disrupts the brain's reward system, making it harder for individuals to resist the allure of food rewards. Additionally, the hormonal imbalance caused by poor sleep can further amplify feelings of hunger and diminish feelings of fullness, making it even more challenging to practice self-control in terms of food choices. To mitigate the adverse effects of sleep deprivationon self-control, several strategies can be implemented. 1. prioritizing sufficient sleep duration is crucial for maintaining cognitive functioning and overall health. Establishing regular sleep patterns and creating a conducive sleep environment can promote better sleep quality. Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques before bedtime can help alleviate stress and promote more restful sleep. Finally, reducing exposure to electronic devices and stimulating activities close to bedtime can enhance sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of late-night snacking episodes. By recognizing the importance of adequate sleep in maintaining self-control and implementing these strategies, individuals can better manage their weight loss goals and make healthier choices throughout the day. Get your Zzz's to avoid those late-night munchies and keep your weight loss goals in check. Avoiding Late-Night Snacking Through Better Sleep Habits When it comes to losing weight, many factors come into play. One often overlooked aspect is the importance of sleep in managing late-night snacking. Understanding the relationship between bedtime and late-night eating is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight. Additionally, sleep deprivation can significantly impact our food choices at night, making us more prone to reaching for unhealthy snacks. In this section, we will dive into strategies for improving our sleep to control late-night snacking, ensuring that our weight loss efforts remain on track. The Relationship Between Bedtime and Late-Night Eating The timing of bedtime has a significant impact on late-night eating habits. Research shows that individuals who go to bed later are more likely to engage in late-night snacking. This relationship between bedtime and late-night eating suggests that the timing of sleep can influence food choices and contribute to weight gain. Furthermore, a study found that delayed bedtimes were associated with increased calorie intake during the evening hours. This means that individuals who stay up later are more likely to consume higher calorie foods during this time period, which can contribute to weight gain over time. In addition, poor sleep quality and duration have been linked to increased cravings for unhealthy foods, such as those high in sugar and fat. This can further contribute to late-night snacking and ultimately lead to weight gain. To address this relationship between bedtime and late-night eating, it is important to prioritize good sleep hygiene practices. Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can help regulate sleep patterns and reduce the likelihood of engaging in late-night snacking. Additionally, creating a relaxing bedroom environment conducive to sleep can promote better quality sleep and reduce the desire for late-night snacks. This includes keeping electronics out of the bedroom, ensuring a comfortable temperature, and minimizing noise and light disturbances. Lastly, practicing stress-reducing activities before bedtime, such as meditation or reading, can help promote better sleep. By managing stress levels, individuals may be less prone to turning to food for comfort or as a coping mechanism during late-night hours. By understanding the relationship between bedtime and late-night eating, individuals can make conscious efforts to improve their sleep habits and reduce the likelihood of unhealthy food choices during these times. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene is crucial for successful weight management. Sleep deprivation turns late-night food choices into a dangerous game of 'Would You Rather' between kale and cookies. How Sleep Deprivation Impacts Food Choices at Night Sleep deprivation has a significant impact on food choices during the night. Lack of sleep can lead to poor decision-making when it comes to selecting what we eat late at night. Research has shown that sleep-deprived individuals are more likely to opt for unhealthy and calorie-dense food options, such as snacks high in sugar and fat. This is due to the negative effects of sleep deprivation on brain responses to food rewards, impairing self-control and increasing cravings for unhealthy foods. Therefore, prioritizing sufficient sleep is crucial in maintaining healthy food choices at night. Previous studies have indicated that sleep deprivation affects various hormones involved in regulating hunger and fullness. Ghrelin, known as the "hunger hormone," increases with lack of sleep, leading to increased appetite. On the other hand, leptin, the hormone responsible for signaling feelings of fullness, decreases with insufficient sleep. These hormonal imbalances contribute to higher hunger levels and less satisfaction from meals, making individuals more susceptible to overeating or indulging in unhealthy late-night snacks. Moreover, poor sleep quality also influences decision-making processes related to food choices. Sleep-deprived individuals tend to have impaired cognitive function and reduced inhibitory control, leading to a greater likelihood of making impulsive decisions regarding their eating habits. They may be more inclined towards choosing instant gratification rather than considering long-term health consequences. One study reported a real-life example of how sleep deprivation impacts food choices at night. Participants who were given limited time for sleep were observed consuming significantly more calories during the evening hours compared to those who had sufficient rest. Furthermore, they tended to consume higher amounts of carbohydrates and fats compared to individuals with adequate sleep duration. Late-night snacking got you down? Improve your sleep to regain control over those midnight munchies! Strategies for Improving Sleep to Control Late-Night Snacking Sleep Optimization Techniques for Managing Late-Night Food Consumption To address the challenge of controlling late-night snacking through improved sleep, a number of effective strategies can be implemented. These strategies aim to optimize sleep quality and duration, thereby reducing the likelihood of engaging in unhealthy eating behaviors during nighttime hours. Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Maintaining a regular sleep routine, including consistent bedtimes and wake-up times, can help regulate circadian rhythms and promote more restful sleep. Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engaging in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading or meditating, can signal the body that it is time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Cultivating a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Creating an optimal sleep environment by ensuring the room is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature can contribute to better quality sleep. Avoiding Stimulants and Electronics Before Bed: Limiting exposure to electronic devices and avoiding stimulants like caffeine or nicotine close to bedtime can facilitate the onset of sleep. By implementing these strategies for improving sleep quality and optimizing bedtime routines, individuals may experience fewer disruptions in their sleep patterns. Consequently, this may reduce late-night cravings for unhealthy snacks and support healthier food choices throughout the day. Furthermore, incorporating adequate physical activity into daily routines has also been shown to enhance overall sleep quality. This may additionally contribute to better control over late-night snacking urges. Conclusion: Prioritizing Sleep for Successful Weight Loss Prioritizing Sleep for Successful Weight Loss Losing weight successfully requires prioritizing sleep. Adequate sleep plays a crucial role in weight loss efforts. It helps regulate hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin, which control appetite and satiety. Lack of sleep disrupts these hormones, leading to increased cravings and appetite, making it harder to stick to a healthy diet. Additionally, sleep deprivation affects metabolism and slows down the rate at which the body burns calories. Therefore, ensuring sufficient sleep is essential for those aiming to achieve successful weight loss. By prioritizing sleep, individuals can optimize their weight loss journey. Sleep deprivation not only affects appetite and metabolism but also impairs cognitive function and decision-making. When sleep-deprived, individuals may be more inclined to make poor food choices and opt for unhealthy, calorie-dense options. On the other hand, getting enough sleep enhances cognitive abilities and self-control, making it easier to make healthy choices and resist temptations. In combination with a balanced diet and regular physical activity, adequate sleep provides a foundation for successful weight loss. It is important to note that prioritizing sleep does not replace the need for healthy eating and regular exercise. Instead, it complements these factors by promoting optimal physical and mental well-being. By incorporating sleep as a priority in weight loss strategies, individuals can achieve long-term success and sustain their progress. Prioritizing sleep is a small yet impactful change that can significantly contribute to overall weight loss efforts. Take control of your weight loss journey by prioritizing sleep. Lack of sleep not only hinders your progress but also increases the risk of weight regain. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to optimize your body's functioning and enhance your weight loss efforts. By committing to adequate sleep, you will not only achieve successful weight loss but also improve your overall health and well-being. Don't let the fear of missing out on sleep sabotage your weight loss goals. 5 Facts About the Importance of Sleep When Losing Weight: ✅ Short sleep duration has been linked to a higher body mass index (BMI) and increased risk of obesity.(Source: Team Research) ✅ Lack of sleep affects hunger hormone levels, increasing appetite and calorie intake. (Source: Team Research) ✅ Poor sleep alters brain function, making it harder to make healthy food choices and resist tempting foods. (Source: Team Research) ✅ Sleep deprivation can lead to increased intake of high calorie, high fat foods. (Source: Team Research) ✅ Going to bed earlier can help avoid late-night snacking and make healthier food choices. (Source: Team Research) FAQs about The Importance Of Sleep When Losing Weight 1. What is the role of sleep in weight management? Getting enough sleep is crucial for weight management. Lack of sleep has been linked to weight gain and an increased likelihood of obesity. It can affect hunger and fullness hormones, leading to increased appetite and cravings for high-fat and high-sugar foods. 2. How does sleep duration affect metabolism? Research has shown that short sleep duration is associated with a higher body mass index (BMI) and weight gain. Lack of sleep can negatively impact the sympathetic nervous system, increase levels of the stress hormone cortisol, and suppress hormones such as insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which is linked to greater fat storage. 3. Can poor sleep quality impact appetite control? Yes, poor sleep quality can affect appetite control. When you don't get adequate sleep, your body produces more of the hunger hormone ghrelin and less of the satiety hormone leptin. This leaves you feeling hungrier and increases your appetite, making it harder to resist tempting foods and make healthier food choices. 4. How does sleep deprivation contribute to weight gain? Sleep deprivation can contribute to weight gain through various mechanisms. It increases appetite, alters decision-making abilities, and enhances the brain's response to food, particularly high-calorie foods. Sleep deprivation may also lead to poorer food choices, including higher intake of foods high in calories, sugar, and fat. 5. What are some healthy sleep habits for weight loss? To support weight loss, it's important to establish healthy sleep habits. Some tips include maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, optimizing sleep environment, avoiding caffeine and electronics before bed, and practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises. 6. How does sleep impact exercise and weight loss? Adequate sleep plays a significant role in exercise and weight loss. It helps with muscle recovery and growth, hormonal balance, and reduces overall stress levels. Getting enough sleep ensures that you have the energy and motivation to engage in regular physical activity, which is essential for weight loss and overall fitness.

